Software as a Service (SaaS) is a cloud-based delivery model that has revolutionized how software is utilized across various industries. By offering software solutions over the cloud, SaaS eliminates the need for businesses to maintain complex hardware setups or manage extensive software systems. Understanding the SaaS deployment models is crucial for organizations looking to leverage these benefits to meet specific requirements. Let’s explore the primary deployment models available and how they cater to diverse organizational needs.
Single-Tenant Model
In the single-tenant model, each client has a dedicated instance of the software. This model is particularly beneficial for organizations that prioritize customization and data isolation. Since each instance is exclusive to a client, businesses can have tailor-made configurations to meet their unique processes and security protocols. This model is often the choice for industries with strict data compliance regulations, where data privacy and security are paramount.
Multi-Tenant Model
The multi-tenant model allows multiple clients to share the same infrastructure and software instance, albeit with separate data partitions. This model is highly efficient as it maximizes resource utilization and minimizes operational costs. It is ideal for organizations that do not have stringent customization needs and are looking for a cost-effective solution. This shared approach also facilitates faster updates and better scalability, as upgrades can be distributed across clients seamlessly.
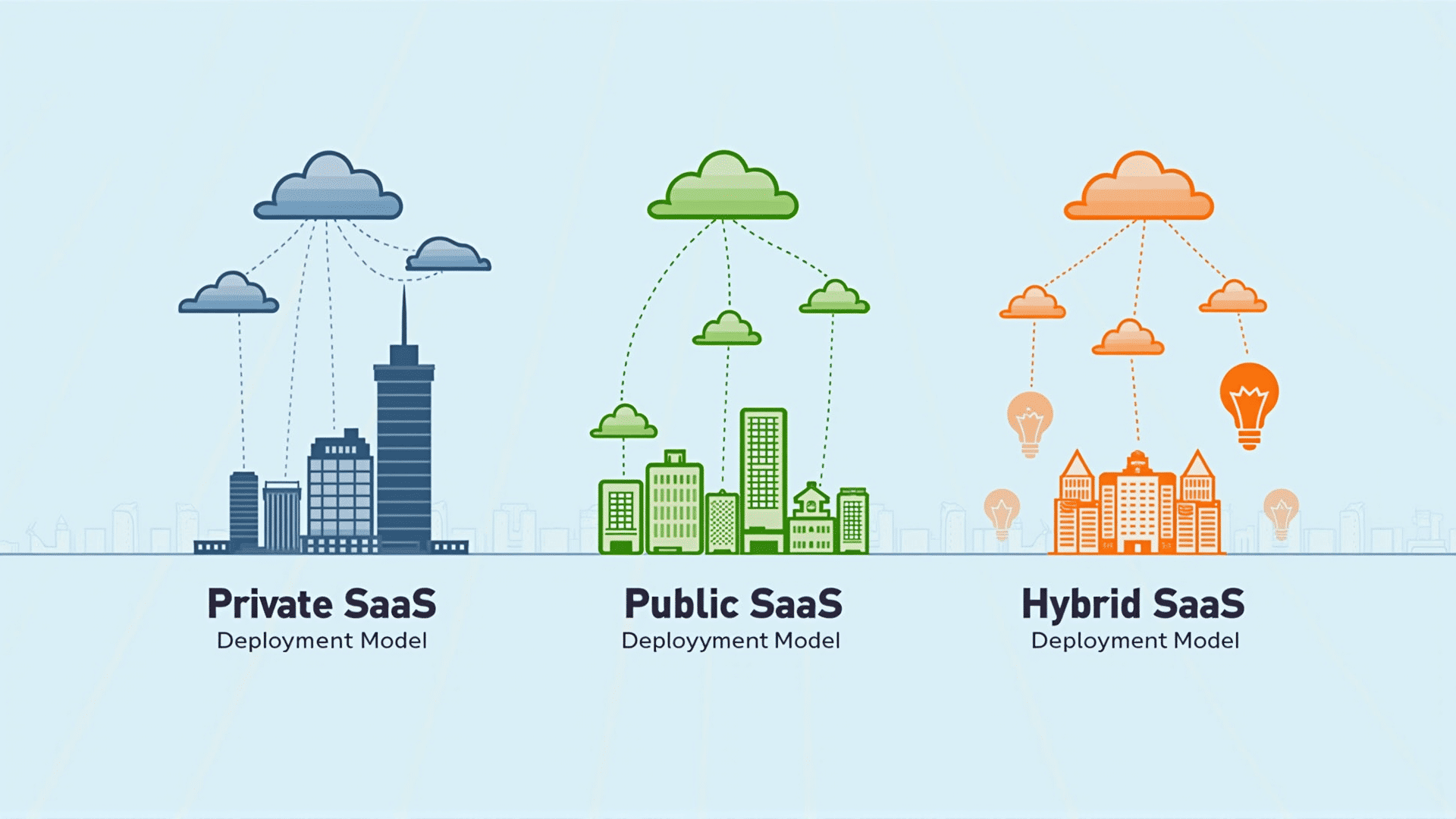
Hybrid Model
The hybrid model combines elements of both single-tenant and multi-tenant scenarios. Organizations can choose which components of their software need individual instances and which can be shared among clients. This model is suitable for businesses that require both extensive customization for certain applications and cost-effective shared options for others. It offers flexibility and allows organizations to optimize performance and cost-efficiency based on their specific requirements.
Private Cloud Model
In a private cloud model, the SaaS is deployed on a dedicated cloud infrastructure for one organization. This approach offers enhanced control, security, and compliance capabilities, making it well-suited for larger enterprises with significant resource allocation needs or those in highly regulated environments. The private cloud model provides organizations with the flexibility to innovate while maintaining stringent controls over the software and its underlying infrastructure.
Public Cloud Model
The public cloud model involves deploying the SaaS on a third-party cloud provider’s infrastructure. This model offers high scalability and reduced overheads, as the service provider manages maintenance, staff, and resources. It supports rapid deployment and can be an excellent choice for businesses that require quick scaling capabilities without investing in extensive infrastructure.
Conclusion
Choosing the right SaaS deployment model largely depends on an organization’s specific needs and constraints, including data privacy, cost considerations, and the degree of control required. Each model offers distinct advantages, and understanding these can help businesses align their IT strategies with their operational goals. By selecting the appropriate deployment model, organizations can optimize their technology infrastructure for enhanced productivity and innovation.